Influenza levels throughout the country are now in the highest ones that have been from the 2009 swine flu peak, according to Figures Published Friday by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in the middle of this winter Second wave of the virus.
About 8% of visits for respiratory diseases to outpatient suppliers, including urgent care and doctors’ offices, informed to CDCs this week were sick people with influenza. That is the worst registered in the influenza surveillance network of the CDC since the end of 2009, during the swine flu pandemic.
While most flu seasons generally see a resurgence of infections after winter holidays, the flu wave this winter has now reached unusually high levels compared to recent years.
That has led General levels of respiratory disease At “very high” levels for the first time this season, despite a smaller and now frequent covid-19 wave in recent months.
Other influenza metrics are also well above recent peaks throughout the country, including In emergency rooms and test laboratories. The data collected by the Laboratory CDCs found that 31.6% of the tests last week were positive for influenza, near the double of 18.2% in the peak last season.
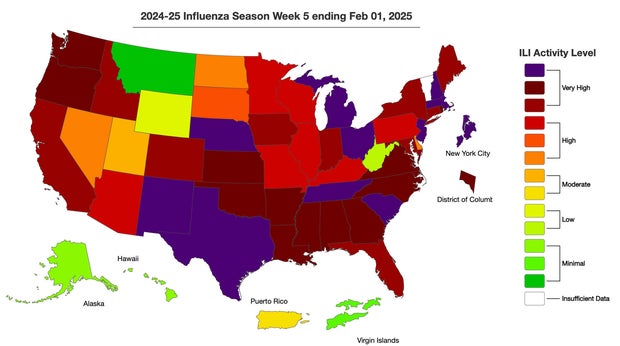
CDC say that most states are at “high” or “very high” levels of influenza activity, although some states may have reached their maximum point.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Influenza infections are “probably growing” in 15 states, the forecasts of the agency’s disease predictAnd now they are flat or begin to decrease in most other states.
Unlike the 2009 pandemic, laboratory tests throughout the country suggest that cases are still of the usual seasonal variants of the virus, and not a new strain that has spilled from animals.
While the farms have been dealing with a wave Aviar H5N1 flu record In birds Conduct egg prices and a new potentially lethal tension In dairy cowsOnly a handful of human cases of aviar flu have been confirmed in the US investigations. They have linked cases to direct contact with sick animals, not in the transmission of humans to humans.